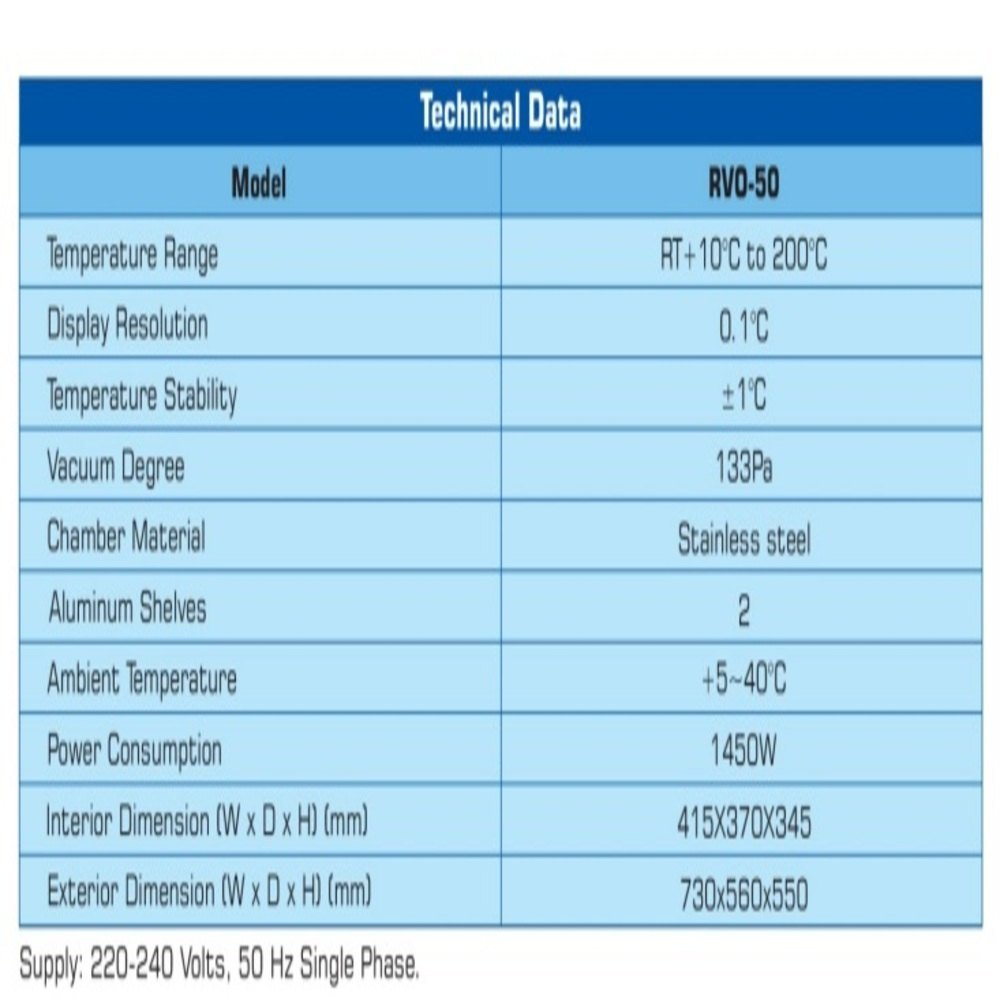
The Role of Hot Air Ovens in Sterilization


A hot oven is laboratory equipment designed to dry and heat materials. Unlike autoclaves that use pressurized steam, hot air ovens utilize circulating air for sterilization. They are commonly used in medical and industrial settings to ensure the cleanliness and safety of equipment and materials. Popular models like the Metalab Digital Hot Air Oven and Remi Dry Hot Air Oven provide precise temperature control and efficient sterilization. Remi Vacuum Ovens offer a controlled environment, ideal for delicate samples.
These ovens like Metalab and Remi are essential in maintaining hygiene and ensuring the safe use of instruments and materials in both clinical and industrial applications. For purchasing and more details, you can find these ovens in medical device apps and medical equipment apps for easy access and comparisons.
Uses and Applications of Hot Air Oven
Hot air ovens serve a variety of application of hot air oven across different fields:
Medical: Used for sterilizing surgical instruments, glassware, and other tools by applying dry heat to kill bacteria and other microorganisms.
Laboratory: Essential for drying samples, sterilizing equipment, and preparing materials that require controlled heat treatment.
Industrial: Used for curing paints and coatings, drying materials, and heat-treating products to achieve specific characteristics, such as hardness or durability.
In medical settings, hot air ovens ensure that surgical instruments are free of any viable microorganisms before being used in procedures, promoting safety and reducing infection risks.
Types of Hot Air Ovens
Benchtop Ovens: Compact and ideal for smaller spaces, benchtop ovens are used for sterilizing equipment, drying samples, and general laboratory use. They are often portable and suitable for low to moderate volumes.
Floor-standing Ovens: Larger and more robust, these ovens are suitable for higher volume sterilization and industrial applications. They offer more space and higher hot air oven temperature capabilities compared to benchtop models.
Gravity Convection Ovens: These ovens rely on natural air circulation (gravity) to distribute heat. They are simple, cost-effective, and commonly used for drying or sterilizing materials that don't require forced air circulation.
Each type varies in size, capacity, and air circulation method, catering to different needs in medical, laboratory, or industrial environments.
Benefits and Advantages of Hot Air Ovens
- It does not require water like an autoclave.
- It is cost-effective and simple to operate.
- It can reach higher hot air oven temperatures and operate faster than autoclaves.
- Its compact size requires less space and is easier to install.
- Dry heat prevents corrosion or rusting of metals and sharp instruments.
- The smaller size makes it convenient for use.
- The low pressure in the oven ensures safe operation.
- It is non-toxic, with no harmful chemical residues.
- Dry heat penetrates deeply into thicker materials, ensuring thorough sterilization.
Directions to use a Hot Air Oven
- Set the temperature according to the items to be sterilized, usually between 160°C to 180°C. Allow the oven to preheat to the set temperature before placing any items inside.
- Clean and dry all items to be sterilized. Ensure they are free of any visible dirt or moisture, as water can interfere with the sterilization process.
- Place the items inside the oven on suitable trays or racks, ensuring they are spaced evenly for proper air circulation. Avoid overcrowding to ensure effective sterilization.
- Adjust the hot air oven temperature to the desired level (usually 160°C to 180°C) and set the timer based on the type of items being sterilized. The typical sterilization time ranges from 30 to 60 minutes, depending on the material.
- Once the oven reaches the desired temperature, start the sterilization process. Monitor the process as needed.
- After the sterilization cycle is complete, allow the items to cool before carefully removing them from the oven. Use heat-resistant gloves or tools to prevent burns.
- After unloading, ensure that all items have been properly sterilized and are free of any contaminants.
Maintenance and Calibration of Hot Air Ovens
- Clean the oven chamber and racks after each use to prevent the buildup of dust, dirt, or residues. Use a mild detergent or alcohol solution to wipe surfaces and ensure all items are free from contaminants. This will prevent cross-contamination during sterilization.
- Perform regular inspections of critical components such as the heating element, fan, and door seals. Look for any signs of wear, corrosion, or physical damage. Inspect the fan for dust or dirt buildup, as this can affect air circulation and heating efficiency. Check the door seals to ensure they are intact and not allowing heat to escape.
- Regularly calibrate the thermostat to ensure accurate temperature readings. This is important for maintaining consistent sterilization conditions and preventing overheating or underheating. A malfunctioning thermostat can result in ineffective sterilization or damage to items being treated.
- If you notice uneven heating, temperature fluctuations, or failure to reach the desired temperature, address the issue promptly. Uneven heating can lead to incomplete sterilization and may cause damage to materials. Ensure that the airflow is not obstructed, and check the temperature sensors for accuracy.
- Periodically check the condition of components like heating elements and thermostats. Worn-out parts should be replaced immediately to maintain proper function and avoid malfunctions.
Safety Considerations for Using Hot Air Ovens
- Always avoid touching the oven's inner surfaces, door, or chamber during and after operation. Use heat-resistant gloves when handling sterilized items.
- Use appropriate PPE, such as gloves and safety glasses, to protect against accidental burns and exposure to high temperatures.
- Adhere to the manufacturer's instructions regarding temperature settings, load capacity, and operating procedures to ensure safe usage. Keep the oven in a well-ventilated area to prevent overheating.
- Ensure the oven is in a well-ventilated area to avoid the buildup of heat and prevent overheating hazards.
Working Principles of a Hot Air Oven
A hot air oven sterilizer operates by using dry heat for sterilization through convection, conduction, and radiation. Heating elements raise the temperature of the air inside the chamber, which is then evenly circulated by fans to expose items to dry heat. This heat first affects the outer surface of the items, and through conduction, it gradually transfers inward. In microorganisms, the heat causes moisture to evaporate, leading to oxidative damage, protein denaturation, disruption of cellular functions, and ultimately, the death of the microorganisms.
Methods for Validating Hot Air Ovens
Validating hot air ovens is crucial to ensure that sterilization is effective and reliable. Validation confirms that the oven consistently reaches the required temperature and maintains it for the necessary duration to eliminate microorganisms.
Methods of validation include:
Biological Indicators: These contain live microorganisms that are resistant to heat. If they are killed during the sterilization process, it confirms that the oven is functioning properly.
Temperature Probes: These are used to monitor and verify the internal temperature at various points inside the oven to ensure uniform heat distribution.
Choosing the Right Hot Air Oven
- Choose based on the amount and size of items you need to sterilize.
- Ensure it can reach the required temperature for your specific sterilization needs (typically 160°C to 180°C).
- Decide between gravity convection (for general use) and forced air (for more uniform heating).
- Choose for models with energy-saving features if budget is a concern.
- Look for ovens with built-in safety features like overheat protection and proper insulation.
- Balance your budget with required features, ensuring you get reliable performance for the cost.
FAQs